What Impacts the Cost of Homeowners Insurance: Key Factors You Should Know
According to NerdWallet, the average annual cost of homeowners insurance in the U.S. is $2,110, or roughly $176 per month. However, what you pay could vary significantly from this figure as insurance companies use a wide range of criteria to determine your premium — from your home’s age, size, and location to your deductible amount and claims history.
In this article, we’ll explore the key factors affecting home insurance costs, what can lead to a home insurance increase, and steps you can take to potentially lower your rate without compromising on protection.
What Impacts Homeowners Insurance Prices?
The cost to insure a home depends on a mix of factors, including where you live. In fact, homeowners insurance costs vary by state due to differences in weather patterns, rebuilding costs, and local crime rates. While your ZIP code can influence your premium, it’s just one of many price considerations. Here are some of the most common factors that affect homeowners insurance premiums.
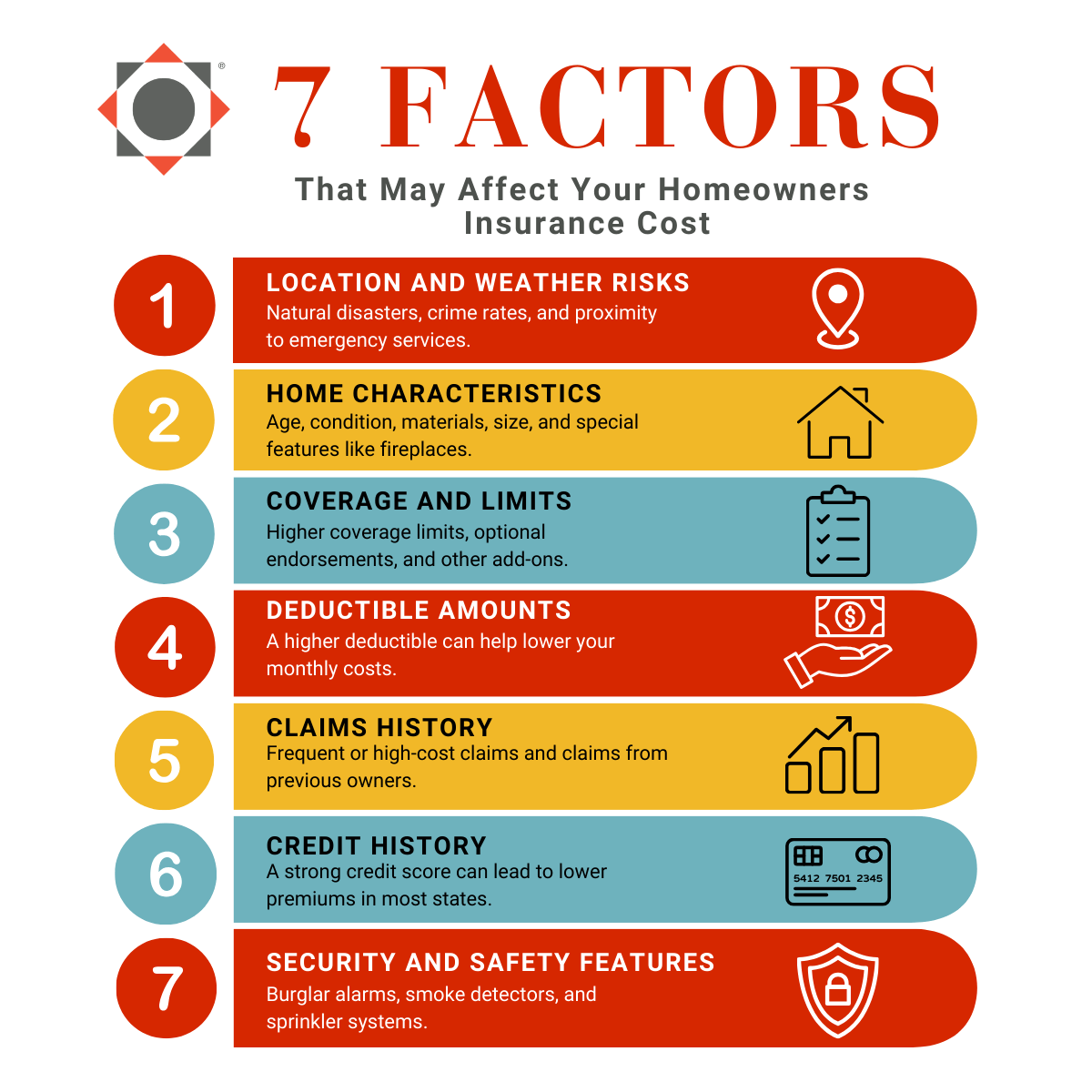
Location and Geographic Risks
The location of your home plays a major role in determining your premium. Areas that are prone to severe weather — storms, high winds, hail, or natural disasters like wildfires, hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes — generally see higher premiums due to the increased risk of damage. Additionally, factors like local crime rates and the proximity of emergency services like fire stations can also impact your premiums.
Home Characteristics
The size, age, condition, and materials of your home can also affect your premium. Older homes often come with outdated electrical, plumbing, or roofing systems, which can increase your insurance costs due to higher repair risks or building code compliance issues. On the other hand, homes constructed with durable, fire-resistant materials may qualify for lower premiums. Additionally, factors like square footage, layout, and special features, such as a finished basement or fireplace, can also shape what you pay.
Coverage and Deductible Selections
Generally, the more coverage you select, the higher your insurance premium will be. Opting for higher limits on your dwelling, personal property, or liability coverage increases your premium, but also provides more robust protection. Similarly, endorsements, which are optional add-on coverages like cyber protection or service line insurance, can raise your total cost but often provide valuable peace of mind.
Your deductible, or the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in, also affects your premium. A lower deductible typically leads to higher premiums, while choosing a higher deductible can help lower your monthly costs. Additionally, some policies may include special deductibles for specific risks, such as wind or hail damage, depending on where you live.
Claims History
A history of frequent or high-cost claims suggests a greater likelihood of future claims, which can lead to higher premiums. Even claims filed by previous owners may affect your property’s insurance profile. In contrast, if you’ve rarely had to file a claim, you may be eligible for discounts or more favorable rates.
Credit History
In most states, insurance companies can use your credit score as a factor in setting your premium. Research shows that individuals with higher credit scores are less likely to file a claim. As a result, maintaining a strong credit score could help you secure more affordable homeowners insurance.
Home Security and Safety Features
Investing in safety upgrades is another great way to potentially reduce both your risk and premium. Features like burglar alarms, smoke detectors, deadbolts, sprinkler systems, and monitored security systems may make you eligible for discounts from your insurance company.
What Causes Homeowners Insurance Cost to Go Up?
Rising insurance premiums can often be influenced by broader industry trends, like inflation, labor shortages, and the increasing frequency of natural disasters, all which can drive up the overall cost of claims. On a more individual level, your premium may also go up based on specific changes in your home, lifestyle, or claims history. Some factors that can raise rate include:
- Adding high-risk features like a pool or trampoline
- Filing multiple claims within a short time period
- Installing home additions or upgrades that increase replacement costs
- Changes in your credit-based insurance score (in some states)
How to Lower Homeowners Insurance Cost
Now that we’ve covered factors that affect homeowners insurance premiums, let’s look at a few ways you might be able to lower your premium:
- Combine your home and auto policies: Take advantage of bundled coverage options like WesPak® and WesPak Estate® to simplify your insurance and save on premiums.
- Increase your deductible: Choose a higher deductible if you’re comfortable with a larger out-of-pocket expense as it can help reduce your monthly premium.
- Upgrade your home security: Install or enhance safety features, such as burglar alarms, smoke detectors, or sprinkler systems.
- Update aging systems: Replace an old roof or outdated systems to lower your risk and potentially reduce your premium.
- Review your policy: Reevaluate your coverage after home improvements or life changes to help ensure you’re not overpaying.
- Inquire about discounts: Ask your insurance agent about available savings for things like being a loyal customer.
Get a Homeowners Insurance Quote
Knowing the factors that affect homeowners insurance premiums can help you make informed, cost-effective decisions. From where you live to the coverage you select, every detail plays a part in what you pay.
At Westfield, we offer flexible coverage designed to fit your lifestyle — whether you’re settling into your first home or looking to protect a longtime investment. Connect with a Westfield insurance agent today for a personalized quote that is tailored to your needs.